Total 234 Questions
Last Updated On : 3-Mar-2026
What happens to the attributes of a Mule event in a flow after an outbound HTTP Request is made?
A. Attributes are replaced with new attributes from the HTTP Request response (which might be null)
B. New attributes may be added from the HTTP response headers, but no headers are ever removed
C. Attributes do not change
D. Previous attributes are passed unchanged
Explanation:
✅ Correct Option
A. Attributes are replaced with new attributes from the HTTP Request response (which might be null) 🟢
When an outbound HTTP Request is made, MuleSoft updates the event’s attributes with details from the HTTP response. These include status code, headers, and other metadata. The previous attributes are completely replaced, not merged. If the HTTP response has no attributes, then the attributes may become null. This ensures that the flow always reflects the latest response context.
❌ Incorrect Options
B. New attributes may be added from the HTTP response headers, but no headers are ever removed 🔴
This is incorrect because MuleSoft does not append attributes. Instead, the original attributes are discarded and replaced. Response headers become the new attributes, meaning old headers are lost, not preserved.
C. Attributes do not change 🔴
This is false. The attributes definitely change because the Mule event is updated with HTTP response attributes. If they did not change, the flow would not be able to handle response metadata such as status codes.
D. Previous attributes are passed unchanged 🔴
This is also incorrect. After an HTTP Request, attributes are not carried forward. They are replaced with new attributes representing the HTTP response. Old attributes are discarded.
📘 Summary:
After an outbound HTTP Request, the Mule event’s attributes are replaced with new attributes from the HTTP response, such as headers and status code. Previous attributes are not preserved. This behavior ensures the flow always works with the most up-to-date response context from the external service.
🔗 Reference:
MuleSoft Documentation – Mule Event Attributes
Refer to the exhibits.
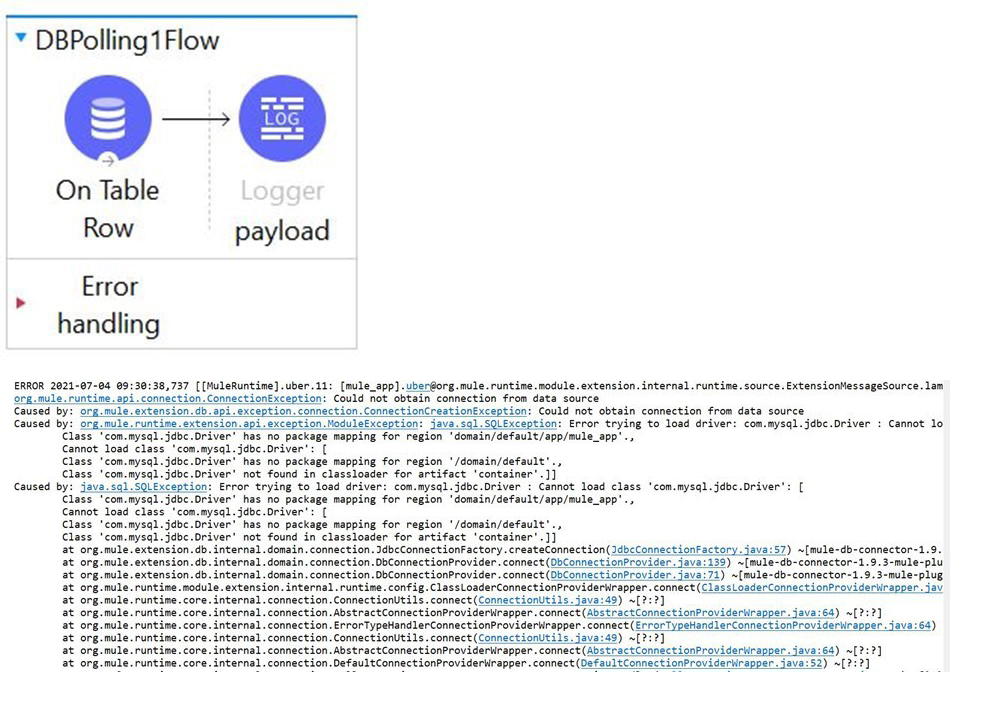
As a mulesoft developer, what you would change in Database connector configuration to resolve this error?
A. Configure the correct host URL
B. Configure the correct database name
C. Configure the correct table name
D. Configure the correct JDBC driver
Explanation:
Correct Option: ✅ D. Configure the correct JDBC driver
The error log indicates a ClassNotFoundException for com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, suggesting the JDBC driver is missing or incorrectly configured. Resolving this requires adding the correct MySQL JDBC driver dependency (e.g., mysql-connector-java) to the Mule application’s pom.xml or ensuring it is included in the project’s classpath. This ensures the database connector can establish a connection to the MySQL database.
Incorrect Options:
❌ A. Configure the correct host URL
While an incorrect host URL can cause connection issues, the error specifically cites a ClassNotFoundException for the JDBC driver, not a connection failure due to host misconfiguration. The issue lies in the driver’s absence, not the host URL. Thus, adjusting the host URL will not resolve the missing driver error.
❌ B. Configure the correct database name
An incorrect database name would typically result in a connection or query error, not a ClassNotFoundException for the JDBC driver. The error indicates the driver class is missing from the classpath, not a database name mismatch. Therefore, configuring the database name is irrelevant to resolving this specific driver-related issue.
❌ C. Configure the correct table name
The table name is irrelevant to the ClassNotFoundException for com.mysql.jdbc.Driver. This error occurs due to the absence of the JDBC driver in the classpath, not a table configuration issue. Adjusting the table name would not address the underlying driver dependency problem causing the connection failure.
Summary:
The scenario involves a Mule application with a database polling flow encountering a ClassNotFoundException for com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, indicating the JDBC driver is missing. The flow attempts to connect to a database and log payload data but fails due to this configuration error. Resolving this requires adding the correct MySQL JDBC driver to the project, ensuring proper database connectivity.
References:
MuleSoft Documentation: Configuring Database Connectors
MuleSoft Documentation: Managing Dependencies
What HTTP method in a RESTful web service is typically used to completely replace an existing resource?
A. GET
B. PATCH
C. PUT
D. POST
Explanation:
✅ Correct Option:
C. PUT
The PUT method is defined by the HTTP specification as idempotent and is used to replace the state of a resource at a known URI with the state defined in the request payload. If a resource exists at that URI, PUT completely overwrites it. If it does not exist, it is often created. This makes it the standard method for a complete update or replacement of an existing resource in RESTful design.
❌ Incorrect Options:
A. GET
The GET method is used solely for retrieving a representation of a resource. It is a safe, read-only operation that must not change the state of the resource on the server, making it unsuitable for any update or replace operation.
B. PATCH
The PATCH method is used for partial updates, not complete replacements. It applies a set of changes described in the request payload to the resource, modifying only the fields that are provided. It is not designed to replace the entire resource.
D. POST
The POST method is a general-purpose operation primarily used to create new resources within a collection. Its behavior is not standardized and is not idempotent. While it can sometimes be used for updates, it is not the standard or recommended method for a complete idempotent replacement of an existing resource.
📋 Summary:
In RESTful API design, HTTP methods have specific semantic meanings. The requirement is to completely replace an existing resource. The PUT method is explicitly designed for this purpose, as it is idempotent and instructs the server to store the enclosed payload at the supplied URI, fully replacing any existing resource there.
🔗 Reference:
RFC 7231, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP/1.1): Semantics and Content, Section 4.3.4 (PUT)
A Utility.dwl file is located in a Mule project at src/main/resources/modules. The Utility.dwl hie defines a function named pascalize that reformats strings to pascal case.
What is the correct DataWeave to call the pascalize function in a Transform Message component?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
Correct Option:
✅ C. Option C
Option C correctly shows the three key components required to call a custom DataWeave function from an external file:
➡️ 1. Importing the module: The import modules::Utility statement correctly imports the Utility.dwl module, specifying the path relative to the src/main/resources directory. The modules:: syntax is the standard way to import a module from the modules directory.
➡️ 2. Calling the function: The Utility::pascalize("max mule") syntax is the correct way to call the imported function. It uses a double colon (::) to reference the function pascalize within the imported Utility module.
➡️ 3. Output and headers: The output application/json and --- separator are standard for a DataWeave script, ensuring the correct output format.
Incorrect Options:
❌ A. Option A
This option incorrectly uses a single dot (.) to import the module (import modules.Utility) and call the function (Utility.pascalize). In DataWeave, the double colon (::) is used for namespacing and referencing modules and their functions. Using a dot is incorrect syntax for both.
❌ B. Option B
This option correctly imports the module (import modules::Utility) but incorrectly calls the function using pascalize("max mule"). When a function is part of an imported module, you must explicitly use the module name as a prefix followed by the double colon (Utility::pascalize). Calling the function without the module prefix would only work if the function were defined directly within the same script, which is not the case here.
❌ D. Option D
This option has two syntax errors. It incorrectly uses a single dot (.) for the import statement (import modules.Utility) and for the function call (Utility.pascalize). As explained above, DataWeave requires the double colon (::) for both importing and calling functions from a module.
Summary:
To call a function from an external DataWeave module, you must first import the module using the import statement with double colons (::) to denote its path (e.g., import modules::Utility). Then, when you call the function, you must qualify the function name with the module name and double colons (e.g., Utility::pascalize("max mule")). This syntax is essential for maintaining proper namespacing and correctly referencing functions within the DataWeave language.
What DataWeave expression transforms the example XML input to the CSV output?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
Explanation:
Correct Option: ✅ D. Configure the correct JDBC driver
The error log indicates a ClassNotFoundException for com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, suggesting the JDBC driver is missing or incorrectly configured. Resolving this requires adding the correct MySQL JDBC driver dependency (e.g., mysql-connector-java) to the Mule application’s pom.xml or ensuring it is included in the project’s classpath. This ensures the database connector can establish a connection to the MySQL database.
Incorrect Options:
❌ A. Configure the correct host URL
While an incorrect host URL can cause connection issues, the error specifically cites a ClassNotFoundException for the JDBC driver, not a connection failure due to host misconfiguration. The issue lies in the driver’s absence, not the host URL. Thus, adjusting the host URL will not resolve the missing driver error.
❌ B. Configure the correct database name
An incorrect database name would typically result in a connection or query error, not a ClassNotFoundException for the JDBC driver. The error indicates the driver class is missing from the classpath, not a database name mismatch. Therefore, configuring the database name is irrelevant to resolving this specific driver-related issue.
❌ C. Configure the correct table name
The table name is irrelevant to the ClassNotFoundException for com.mysql.jdbc.Driver. This error occurs due to the absence of the JDBC driver in the classpath, not a table configuration issue. Adjusting the table name would not address the underlying driver dependency problem causing the connection failure.
Summary:
The scenario involves a Mule application with a database polling flow encountering a ClassNotFoundException for com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, indicating the JDBC driver is missing. The flow attempts to connect to a database and log payload data but fails due to this configuration error. Resolving this requires adding the correct MySQL JDBC driver to the project, ensuring proper database connectivity.
References:
MuleSoft Documentation: Configuring Database Connectors
MuleSoft Documentation: Managing Dependencies
Refer to the exhibit.
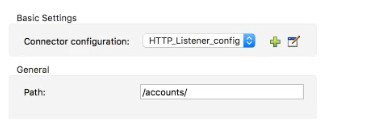
What is the correct syntax to add an employee ID as a URI parameter in an HTTP Listener path?
A. (employeelD)
B. ${emp!oyeelD}
C. {employeelD}
D. # [employeelD]
Explanation:
Correct Option:
✅ C. {employeeID}
In Mule 4's HTTP Listener, URI parameters are defined using a pair of curly braces {}. This syntax indicates that the path segment is a variable that will capture a value from the incoming request's URI. For example, if the path is /accounts/{employeeID}, and an incoming request is sent to /accounts/12345, the value 12345 will be captured and stored in a variable named employeeID. This variable can then be accessed later in the flow using the expression attributes.uriParams.employeeID.
Incorrect Options:
❌ A. (employeeID)
This syntax is not the correct way to define a URI parameter in Mule's HTTP Listener. Parentheses () are not used for this purpose in Mule 4. This syntax would likely be interpreted as a literal part of the path, not as a placeholder.
❌ B. ${employeeID}
This is the syntax for a placeholder property, which is used to externalize configuration values in a Mule application (e.g., in a config.yaml file). It is not used to define URI parameters within the HTTP Listener's path field.
❌ D. #[employeeID]
This is the syntax for a DataWeave expression. While you would use this syntax to access the URI parameter value later in your flow (e.g., #[attributes.uriParams.employeeID]), it is not the correct syntax for defining the parameter itself in the HTTP Listener's Path configuration field.
Summary:
To define a URI parameter in an HTTP Listener path in Mule 4, you must use curly braces {}. This syntax tells the listener to treat the enclosed name as a variable that will capture a value from the incoming request's URI. After the value is captured, it becomes available in the attributes.uriParams object, and you can access it within your Mule flow using a DataWeave expression like #[attributes.uriParams.employeeID].
Which keyword do you use to create a new function in DataWeave?
A. function
B. fun
C. func
D. map
Explanation:
✅ Correct Option:
B. fun
In DataWeave, the keyword fun is used to define a new function. This is the official and syntactically correct declarative keyword for creating anonymous functions, which can be assigned to variables or used inline. For example: var myFunction = fun(x) -> x * 2.
❌ Incorrect Options:
A. function
This is incorrect. While function is a common keyword in many other programming languages like JavaScript, it is not the keyword used for function definition in the DataWeave language. Using function will result in a syntax error.
C. func
This is incorrect. func is an abbreviation sometimes used in other languages but is not valid syntax in DataWeave. The language specification requires the use of fun to declare a function.
D. map
This is incorrect. map is a higher-order function in DataWeave used to apply a transformation to every element of an array. It is not a keyword for creating a new function but rather a function that consumes another function as an argument.
📋 Summary:
DataWeave has its own specific syntax for function definition. To create an anonymous function, the correct and required keyword is fun, followed by the parameters and the function body. This is a fundamental part of the language's syntax for defining reusable transformation logic.
🔗 Reference:
MuleSoft Documentation: DataWeave - Functions (The documentation shows examples using the fun keyword).
A Mule flow has three Set Variable transformers. What global data structure can be used to access the variables?
A. Mule event attributes
B. Mule event message
C. Mule application properties
D. Mule event
Explanation:
Correct Option: ✅ D. Mule Event
The Mule Event is the global data structure that encapsulates the entire context of a Mule flow, including the message and attributes. Set Variable transformers store variables within the Mule Event, making them accessible throughout the flow using vars.variableName. This structure ensures variables set by transformers are available for subsequent processing, providing a unified access point within the flow.
Incorrect Options:
❌ A. Mule event attributes
Mule event attributes are part of the Mule Event but specifically store metadata (e.g., headers, error information), not variables set by Set Variable transformers. Variables are stored in the Mule Event’s vars scope, not attributes, making this option incorrect for accessing variables set in the flow.
❌ B. Mule event message
The Mule event message contains the payload and properties, but variables set by Set Variable transformers are stored in the Mule Event’s vars scope, not the message. Accessing variables through the message is incorrect, as the message is designed for payload and property data, not variable storage.
❌ C. Mule application properties
Mule application properties are configuration settings defined outside the flow (e.g., in properties files), not variables set by transformers. They are accessed via app.properties, distinct from flow-specific variables. Thus, this option is incorrect for accessing variables within the Mule flow.
Summary:
The scenario involves a Mule flow with three Set Variable transformers, which set variables during execution. The Mule Event serves as the global data structure, containing the vars scope where these variables are stored. This allows access to variables (e.g., vars.variableName) throughout the flow, ensuring consistent data management and availability for subsequent processors.
References:
MuleSoft Documentation: Mule Event
MuleSoft Documentation: Variables in Mule
An API instance of type API endpoint with API proxy is created in API manager using an API specification from Anypoint Exchange. The API instance is also configured with an API proxy that is deployed and running in CloudHub.
An SLA- based policy is enabled in API manager for this API instance.
Where can an external API consumer obtain a valid client ID and client secret to successfully send requests to the API proxy?
A. In the organization's public API portal in Anypoint Exchange, from an approved client application for the API proxy
B. In Anypoint Studio, from components generated by APIkit for the API specification
C. In Anypoint Studio, from components generated by Rest Connect for API specification
D. In Runtime Manager, from the properties tab of the deployed approved API proxy
Explanation:
✅ Correct Option
A. In the organization's public API portal in Anypoint Exchange, from an approved client application for the API proxy 🟢
When an SLA-based policy (like Rate Limiting or Throttling) is applied, MuleSoft enforces client ID and client secret validation. These credentials are issued when an external API consumer registers their client application through the API portal in Anypoint Exchange. Once the application is approved, the client gets a valid client ID and client secret to access the API proxy successfully.
❌ Incorrect Options
B. In Anypoint Studio, from components generated by APIkit for the API specification 🔴
APIkit scaffolds flows in Anypoint Studio based on the API specification, but it does not provide client credentials for consumers. It is a developer tool for building APIs, not a distribution point for consumer authentication details.
C. In Anypoint Studio, from components generated by Rest Connect for API specification 🔴
Rest Connect helps generate reusable connectors from REST APIs but does not issue client IDs or secrets. Like APIkit, it is focused on simplifying integration, not consumer identity management.
D. In Runtime Manager, from the properties tab of the deployed approved API proxy 🔴
Runtime Manager shows deployment properties, logs, and monitoring details, but it does not provide client credentials. Only Anypoint Exchange, via the API portal, manages client applications and their credentials.
📘 Summary
In this case, the API proxy is deployed in CloudHub and protected by an SLA-based policy. API consumers must obtain valid client credentials. These credentials are created when the consumer registers and gets approval for their client application in the organization’s API portal in Anypoint Exchange. This ensures controlled and secure access to the API proxy.
🔗 Reference
MuleSoft Documentation – Managing Client Applications
Refer to the exhibit. The main flow contains an HTTP Request in the middle of the flow. The HTTP Listeners and HTTP request use default configurations.
What values are accessible to the Logger at the end of the flow after a web client submit request to http://local:801/order?color=red?
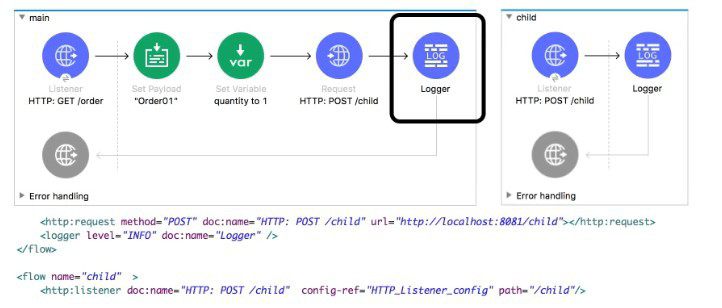
A. payload
B. payload quantity var
C. payload color query param
D. payload quantity var color query param
Explanation:
✅ Correct Option:
A. payload
After the HTTP Request operation completes, the Mule event is replaced by the response from the called endpoint. The Logger at the end of the main flow will only have access to the payload from the HTTP response. The original variables (like quantity) and the original attributes (like the color query param) from the initial request are not part of this new event created by the HTTP response.
❌ Incorrect Options:
B. payload quantity var
This is incorrect. While the quantity variable was set in the main flow, the HTTP Request operation does not preserve the original variables in the outbound event. The event after the HTTP Request is a new event containing only the response payload and its associated attributes, not the original flow's variables.
C. payload color query param
This is incorrect. The color query parameter was part of the original request's attributes. The HTTP Request operation replaces the original attributes with the attributes of the HTTP response it received. The response from the /child endpoint does not contain the original query parameter, so it is inaccessible.
D. payload quantity var color query param
This is incorrect for the combined reasons above. The Logger's event is the result of the HTTP Request call. This new event contains only the response payload. It does not contain the original quantity variable or the original color query parameter from the initial request to the main flow.
📋 Summary:
An HTTP Request operation replaces the entire Mule event with the response from the called HTTP resource. The logger at the end of the flow only sees this new event. Therefore, it can only access the payload from the child flow's response. The original variable (quantity) and request attribute (the color query parameter) are lost from the event context at this point.
🔗 Reference:
MuleSoft Documentation: HTTP Request Operation
| Page 2 out of 24 Pages |
| 12345678 |
| Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer Practice Test Home |
Our new timed 2026 Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer practice test mirrors the exact format, number of questions, and time limit of the official exam.
The #1 challenge isn't just knowing the material; it's managing the clock. Our new simulation builds your speed and stamina.
You've studied the concepts. You've learned the material. But are you truly prepared for the pressure of the real Salesforce Certified MuleSoft Developer - Mule-Dev-201 exam?
We've launched a brand-new, timed Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer practice exam that perfectly mirrors the official exam:
✅ Same Number of Questions
✅ Same Time Limit
✅ Same Exam Feel
✅ Unique Exam Every Time
This isn't just another Salesforce-MuleSoft-Developer practice questions bank. It's your ultimate preparation engine.
Enroll now and gain the unbeatable advantage of: