Total 202 Questions
Last Updated On : 20-Feb-2026
A client sells its product in single-brand stores as well as in multi-brand stores. When shown in the store
locator list, the client wants the single-brand stores to have a particular background color to highlight them.
Which Business Manager action should be completed to allow the developer to apply different styling to the single-brand stores?
A. Add a Boolean custom attribute to the Store system object
B. Configure the existing Store custom object type definition
C. Create a new SingleBrandStore custom object configuration
D. Adjust the relevant Site Preference in the Stores group
Explanation:
The requirement calls for distinguishing between single-brand and multi-brand stores in the store locator for styling purposes. The most efficient and architecturally sound approach is to extend the existing Store system object with a custom attribute. B2C Commerce allows developers to add custom attributes to system objects like Store through Business Manager. By creating a Boolean custom attribute (e.g., isSingleBrand), merchants can flag each store accordingly. This attribute then becomes available in the store data model, enabling the front-end developer to access it via the Store API and apply conditional CSS classes or inline styles in the store locator ISML template. For instance, in the template, one could write:
A developer is given a task to implement a new Page Designer layout component that doesn’t accept certain asset components.How should the developer achieve the above task?
A. Add component_type_inclusion in the layout json configuration
B. Add component_type_Exclusions in the layout json configuration
C. Add layout_type_inclusion in the target components json configurations.
D. Add layout_type_exclusion in the other asset components json configuration
Explanation:
Why B is correct
Page Designer layout components in SFCC allow fine-grained control over which component types (assets) can be dropped inside them. This is configured directly in the layout component's JSON configuration file (e.g., my-layout.json). The key component_type_exclusions is an array of component type IDs that are explicitly forbidden from being added to this layout. This is the official, recommended way to restrict content types inside specific layouts (introduced and documented since SFRA 3+ / Page Designer 2.x).
Why the other options are incorrect
A. Add component_type_inclusion in the layout json configuration
There is no key called component_type_inclusion in layout configuration. Inclusion is the default behavior — you exclude what you don’t want.
C. Add layout_type_inclusion in the target components json configurations
Components do not control which layouts they can go into. The control direction is layout → allowed/excluded components, not the other way around.
D. Add layout_type_exclusion in the other asset components json configuration
Same conceptual error as C. Asset components should not define layout restrictions — that responsibility belongs to the layout.
References
Salesforce Commerce Cloud Documentation → Page Designer → Component Configuration Schema
Developer Guide: "Restricting Component Usage in Layouts" section
Universal Containers needs to have Apple Pay disabled for the country of Spain.
Which Business Manager module should the Developer use to meet this requirement?
A. Merchant Tools > Ordering > Payment Methods
B. Merchant Tools > Site Preferences > Apple Pay
C. Merchant Tools > Ordering > Payment Processors
D. Merchant Tools > Site Preferences > Payment Types
Explanation:
In Salesforce B2C Commerce, the Payment Methods module is the central hub for managing which payment options (Credit Card, PayPal, Apple Pay, etc.) are available to customers.
When you open a specific Payment Method (like Apple Pay) in this module, you can configure its Country Restrictions. By selecting Spain in the exclusion list or ensuring it isn't in the inclusion list, the platform automatically suppresses Apple Pay as an option for any customer whose basket or session is associated with that country. This is the standard, out-of-the-box way to handle regional payment compliance without writing custom code.
Why the Incorrect Answers are Wrong
B. Merchant Tools > Site Preferences > Apple Pay: While some global Apple Pay settings (like Merchant ID) are found here, the actual enablement, sequencing, and regional availability of the payment option are handled in the Ordering module.
C. Merchant Tools > Ordering > Payment Processors: Payment Processors define the "Engine" (e.g., CyberSource, Adyen) that handles the transaction. While you can associate a method with a processor, the logic of "Do not show this to users in Spain" is a function of the Payment Method configuration, not the Processor itself.
D. Merchant Tools > Site Preferences > Payment Types: "Payment Types" is not a standard module path for managing country-level availability in the B2C Commerce Business Manager.
References
Managing Payment Methods
Apple Pay for B2C Commerce Guide
Universal Containers recently completed updates to their storefront shopping cart page. A
problem has been discovered since the update. Users are no longer able to submit coupon
codes on this page. Additionally, authenticated userswho try to add a coupon are logged
out.
The following processing code is found in the Cart.js controller file:
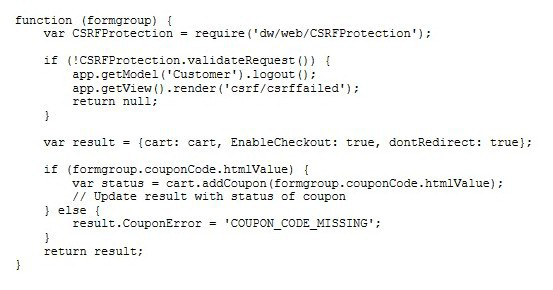
What should the Developer verify to identify the issue?
A. The CSRF cartridge is included in the site’s cartridge path
B. The form group has the secure attribute set to true
C. The CSRF token is present in the form and is being submitted in the request.
D. The CSRF settings in Business Manager are properly configured.
Explanation:
The symptoms described point clearly to a CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) protection failure:
Coupon form fails to submit
Authenticated users are logged out when submitting the form
This is a common result of missing or invalid CSRF tokens. In SFRA (Salesforce Reference Architecture), CSRF protection is enabled by default on forms that use POST, and failure to validate a CSRF token will cause:
Form submission to be rejected
Session to be invalidated (causing logout)
✅ What to Verify:
You should inspect the ISML template that renders the coupon submission form and ensure it includes this hidden input:
This injects the valid CSRF token into the form using the csrf object available in the pipeline dictionary.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. The CSRF cartridge is included in the site’s cartridge path
➤ CSRF isn’t a standalone cartridge — it’s a middleware provided in SFRA, not a separate cartridge.
B. The form group has the secure attribute set to true
➤ secure="true" ensures the form is submitted via HTTPS, but does not affect CSRF handling.
D. The CSRF settings in Business Manager are properly configured
➤ CSRF settings in BM are rarely the cause — they only define global enforcement, and won’t override missing token logic in your ISML or controller.
A Digital Developer suspects a logical error in a script.
Which action will help locate the error?
A. Submit a support ticket to B2C Commerce.
B. Check request logs for evidence of the logical error.
C. Put breakpoints in the code, debug, and examine variable values.
D. Print all values in the script node called before the current script.
Explanation:
Logical errors are flaws in program flow or business logic that produce incorrect results while the code still executes without syntax errors. The most effective way to locate these is through interactive debugging. B2C Commerce provides debugging tools in UX Studio and Business Manager Script Debugger that allow developers to:
- Set breakpoints at suspicious lines of code
- Step through execution line by line
- Inspect variable values at runtime
- Watch expressions evaluate in real-time
- Trace call stacks to understand execution flow
This approach directly addresses logical errors by revealing the actual state of the program versus expected state. For example, if a conditional statement isn't branching correctly, examining the variables at the breakpoint shows whether the condition evaluates as anticipated. Debugging provides definitive insight into runtime behavior that static code analysis or logging cannot match in efficiency.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
A. Submit a support ticket to B2C Commerce – Support tickets are for platform issues, bugs, or outages, not for debugging custom code logic. Salesforce support won't analyze business logic errors in customer implementations.
B. Check request logs for evidence of the logical error – Logs may show symptoms (like incorrect data being processed) but rarely reveal the root cause of logical errors. Logical errors often produce valid-looking requests with wrong business outcomes that aren't logged as errors.
D. Print all values in the script node called before the current script – This is a primitive form of logging that could generate excessive noise. While sometimes useful, it's less efficient than targeted debugging and may not capture the exact moment the logical error occurs.
References
B2C Commerce Debugging Guide: "Using the Script Debugger"
UX Studio Documentation: "Debugging Techniques"
Salesforce Help Article: "Troubleshooting Logic Errors in Scripts"
A Digital Developer is adding support for an additional language other than the default. The locale code for
the new language is de.
In which folder should the developer place resource bundles?
A. templates/de
B. templates/default
C. templates/resources
D. templates/default/resources
Explanation:
In B2C Commerce, localized storefront text is typically stored in properties files known as resource bundles (template resource bundles). These are accessed from ISML via Resource.msg(...) and similar methods. For SFRA and many storefront implementations, the standard location for these bundles is the /templates/resources directory, and the locale is typically expressed in the filename suffix (for example account_de.properties, account_de_DE.properties), or through directory structure depending on the project pattern.
Salesforce Trailhead guidance for localizing storefront components explicitly describes storing resource bundles under /templates/resources and specifying locale codes in filenames (examples include account_en_US.properties). The dw.web.Resource API documentation also confirms that the platform loads locale-specific strings from resource bundles appropriate for the current locale. Therefore, to add German (de), the correct answer among the provided options is templates/resources, because that is where template resource bundles are stored and resolved.
The other listed directories either refer to template sets (templates/default) or to locale-specific template folders for ISML templates themselves — not the resource bundle location. Resource bundles are not placed in templates/default/resources as a standard pattern in SFRA; instead, resources are centralized in templates/resources and then differentiated by filename.
Why the other options are incorrect
A. templates/de — That resembles a locale template folder for ISML templates, not where .properties bundles go.
B. templates/default — This is where default-locale ISML templates reside, not resource bundles.
D. templates/default/resources — Not the documented standard location for template resource bundles in the modern pattern; you’d typically use templates/resources.
References
Trailhead: localize storefront components; resource bundles under /templates/resources with locale filenames
dw.web.Resource API (resource bundles provide locale-specific strings)
Templates are stored under locale folders; separate concept from resource bundles
A Digital Developer is tasked with setting up a new Digital Server Connection using UX Studio in their
sandbox.
Which three items are required to accomplish this task? (Choose three.)
A. Instance Version
B. Instance Hostname
C. Business Manager Username
D. Keystore Password
E. Business Manager Password
Explanation:
Why These Answers Are Correct
Setting up a Digital Server Connection in UX Studio requires authentication credentials and connection details to establish a secure link between the local development environment and the remote B2C Commerce instance. The three essential items are:
B. Instance Hostname – The URL of the target instance (e.g., dev01-realm.demandware.net). This tells UX Studio where to connect.
C. Business Manager Username – A valid BM account with appropriate permissions (typically Developer role or higher) to authorize the connection and perform operations like code deployment.
E. Business Manager Password – The corresponding password for authentication.
These credentials are entered in UX Studio's connection wizard, which establishes an authenticated WebDAV connection for file transfer and may use SOAP or REST APIs for additional operations. The connection allows developers to upload cartridges, import data, and synchronize changes between local and remote environments.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
A. Instance Version – While useful information, the instance version isn't required to establish the connection. UX Studio can detect version information after connecting, or it may be automatically determined during the handshake.
D. Keystore Password – Keystore passwords are for certificate management and SSL configurations, not for basic Digital Server Connections. They might be needed for specific advanced configurations but aren't among the three essential items.
References
UX Studio Installation and Setup Guide: "Configuring Server Connections"
B2C Commerce Developer Onboarding: "Connecting Development Environments"
A Digital Developer has been given a specification to integrate with a REST API for retrieving weather
conditions. The service expects parameters to be form encoded.
Which service type should the Developer register?
A. FTP
B. SOAP
C. HTTP Form
D. WebDAV
Explanation:
When integrating with a REST API that expects parameters to be "form-encoded" (this corresponds to the Content-Type application/x-www-form-urlencoded), the Developer should use the HTTP Form service type.
In the B2C Commerce Service Framework, choosing "HTTP" allows for standard RESTful interactions. However, the "Form" designation specifically tells the framework how to package the body of the request. Since weather services and many legacy REST APIs require parameters to be sent as key-value pairs in the body (similar to an HTML form submission), this service type provides the correct helper methods to serialize the data properly.
Why the Incorrect Answers are Wrong
A. FTP – File Transfer Protocol is used for moving large files (like catalogs or price books) between servers. It cannot be used to call a REST API for real-time data like weather.
B. SOAP – Simple Object Access Protocol is an XML-based protocol. If a service is "REST," it by definition is not SOAP. Using a SOAP service type would result in the wrong headers and envelope structure.
D. WebDAV – This is used primarily for managing the instance file system (uploading logs, static files, or code). It is not intended for external 3rd-party API integrations.
References
B2C Commerce Service Framework
Integrating External Web Services
Given a NewsletterSubscription custom object that has a key attribute named email of type String, what is the correct syntax to create the NewsletterSubscription custom object and persist it to the database?
A. Var customobject = dw.object.CustomObjectMgr.createNewsletterSubscription(‘email’, newsLetterForm.email.value);
B. Var customobject = dw.object.CustomObjectMgr.createCustomObject(newsletterForm.email.value, ‘NewsletterSubscription’)
C. Var customobject = dw.object.CustomObjectMgr. createCustomObject (‘NewsletterSubscription’, newsLetterForm.email.value);
D. Var customobject = dw.object.CustomObjectMgr. createCustomObject (‘NewsletterSubscription’,’email’, newsLetterForm.email.value);
Explanation:
Creating and persisting a custom object in Salesforce B2C Commerce requires using the dw.object.CustomObjectMgr API. The method createCustomObject(type, key) is the standard way to instantiate a new custom object. Let’s break this down carefully:
Custom Object Type: This is the identifier of the custom object definition created in Business Manager. In this case, the type is "NewsletterSubscription".
Key Value: Every custom object requires a unique key. For the NewsletterSubscription object, the key attribute is email (of type String). When creating the object, you pass the actual value of the email field from the form, e.g., newsLetterForm.email.value.
Thus, the correct syntax is:
var customobject = dw.object.CustomObjectMgr.createCustomObject('NewsletterSubscription', newsLetterForm.email.value);
This ensures the object is created and persisted in the database with the email as its unique key.
Why Option C is Correct
- It uses the correct method: createCustomObject(type, key).
- It passes the type first ('NewsletterSubscription') and then the key value (newsLetterForm.email.value).
- This matches the documented API signature and ensures proper persistence.
Why the Other Options Are Incorrect
A. createNewsletterSubscription('email', newsLetterForm.email.value')
There is no such method as createNewsletterSubscription. The API only provides createCustomObject.
B. createCustomObject(newsletterForm.email.value, 'NewsletterSubscription')
The arguments are reversed. The first argument must be the type (NewsletterSubscription), not the key.
D. createCustomObject('NewsletterSubscription','email', newsLetterForm.email.value')
The method only accepts two arguments (type and key). Adding a third argument is invalid and will throw an error.
Reference
Salesforce B2C Commerce Developer Documentation – Custom Objects:
“Use dw.object.CustomObjectMgr.createCustomObject(type, key) to create and persist a custom object. The first parameter is the custom object type ID, and the second is the unique key value.”
Salesforce Developer Guide on Custom Objects
Which three operations should be done in a controller?
Choose 3 answers
A. Generate the response as JSON or HTML
B. Use the Script API to generate data for the view.
C. Use middleware functions when applicable
D. Create a plain JavaScript object representing a system object
Use the model needed for the view.
Explanation:
Controllers in B2C Commerce's MVC architecture have specific responsibilities:
A. Generate the response as JSON or HTML – Controllers are responsible for final output generation. They determine the response format based on the request (e.g., AJAX calls return JSON, regular requests return HTML via ISML templates). This is done using res.json() for API endpoints or res.render() for views.
B. Use the Script API to generate data for the view – Controllers interact with B2C Commerce's Script API to fetch and process data from the platform (products, carts, customers, etc.), then prepare this data as a pipeline dictionary for the view. This is the "M" in MVC—preparing the model.
C. Use middleware functions when applicable – B2C Commerce controllers support middleware patterns through functions like server.get() with multiple handler functions. Middleware handles cross-cutting concerns like authentication, logging, or validation before reaching the main controller logic, promoting code reuse and separation of concerns.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
D. Create a plain JavaScript object representing a system object – This describes data modeling, not a controller responsibility. System objects are represented by platform classes (like dw.catalog.Product), not plain JavaScript objects. Creating plain objects would lose all platform functionality.
E. Use the model needed for the view – While controllers prepare data for views, this phrasing is vague and overlaps with option B. More precisely, controllers prepare and provide the model; they don't "use" it in the same sense.
References
B2C Commerce MVC Architecture Documentation: "Controller Responsibilities"
Developer Guide: "Controller Patterns and Best Practices"
Script API Guide: "Data Access in Controllers"
Middleware Documentation: "Using Pipeline Functions in Controllers"
| Page 3 out of 21 Pages |
| 1234567 |
| Salesforce-B2C-Commerce-Cloud-Developer Practice Test Home |
Our new timed Salesforce-B2C-Commerce-Cloud-Developer practice test mirrors the exact format, number of questions, and time limit of the official exam.
The #1 challenge isn't just knowing the material; it's managing the clock. Our new simulation builds your speed and stamina.
You've studied the concepts. You've learned the material. But are you truly prepared for the pressure of the real Salesforce Certified B2C Commerce Cloud Developer - Comm-Dev-101 exam?
We've launched a brand-new, timed Salesforce-B2C-Commerce-Cloud-Developer practice exam that perfectly mirrors the official exam:
✅ Same Number of Questions
✅ Same Time Limit
✅ Same Exam Feel
✅ Unique Exam Every Time
This isn't just another Salesforce-B2C-Commerce-Cloud-Developer practice questions bank. It's your ultimate preparation engine.
Enroll now and gain the unbeatable advantage of: